ELECFREAKS Micro:bit XGO Rider Self-Balancing Robot
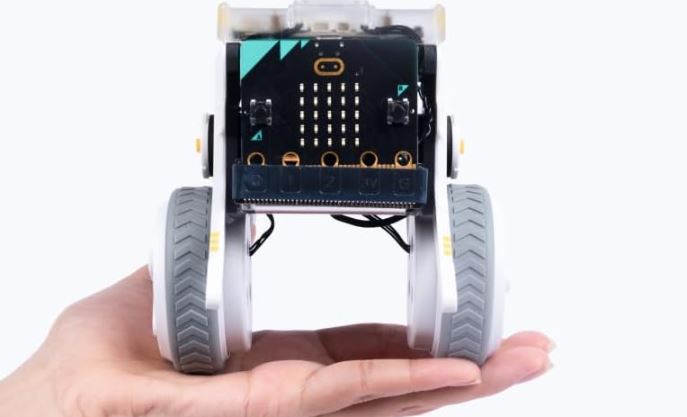
micro:bit is a wonderful platform for building and programming educational robots. The ELECFREAKS Micro:bit XGO Rider is a self-balancing robot powered by it. It is ready for graphical and Python programming. This robot is compact enough to fit on the palm of your hand. It can be controlled with a smartphone or micro:bit powered joystick.
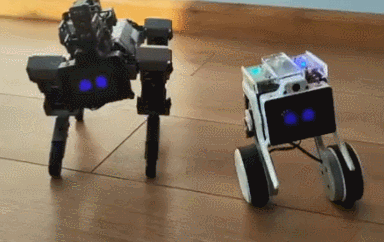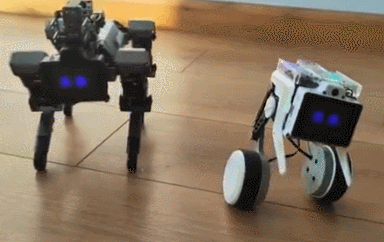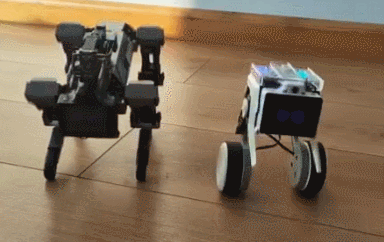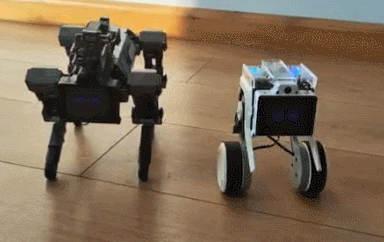
The XGO Rider ships assembled. It has brushless motors and all-metal servos for smooth performance. The battery lasts up to 3 hours.







































![NexusBot Programmable Robot [Python, MakeCode]](https://www.roboticgizmos.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/10/Bosvision-NexusBot-Programmable-Robot-100x75.jpg)



